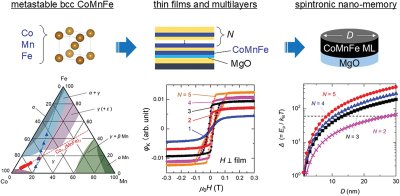
Novel film with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy could boost spintronics memory
A team of Tohoku University researchers recently investigated a cobalt-manganese-iron alloy thin film that demonstrates a high perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA) - key aspects for fabricating MRAM devices using spintronics.
"This is the first time a cobalt-manganese-iron alloy has strongly shown large PMA," says Professor Shigemi Mizukami from Tohoku University, "We previously discovered this alloy showed a high tunnel magnetoresistance (TMR) effect, but it is rare that an alloy potentially shows both together." For example, Iron-cobalt-boron alloys, which are conventionally used for MRAM, possess both traits, but their PMA is not strong enough.